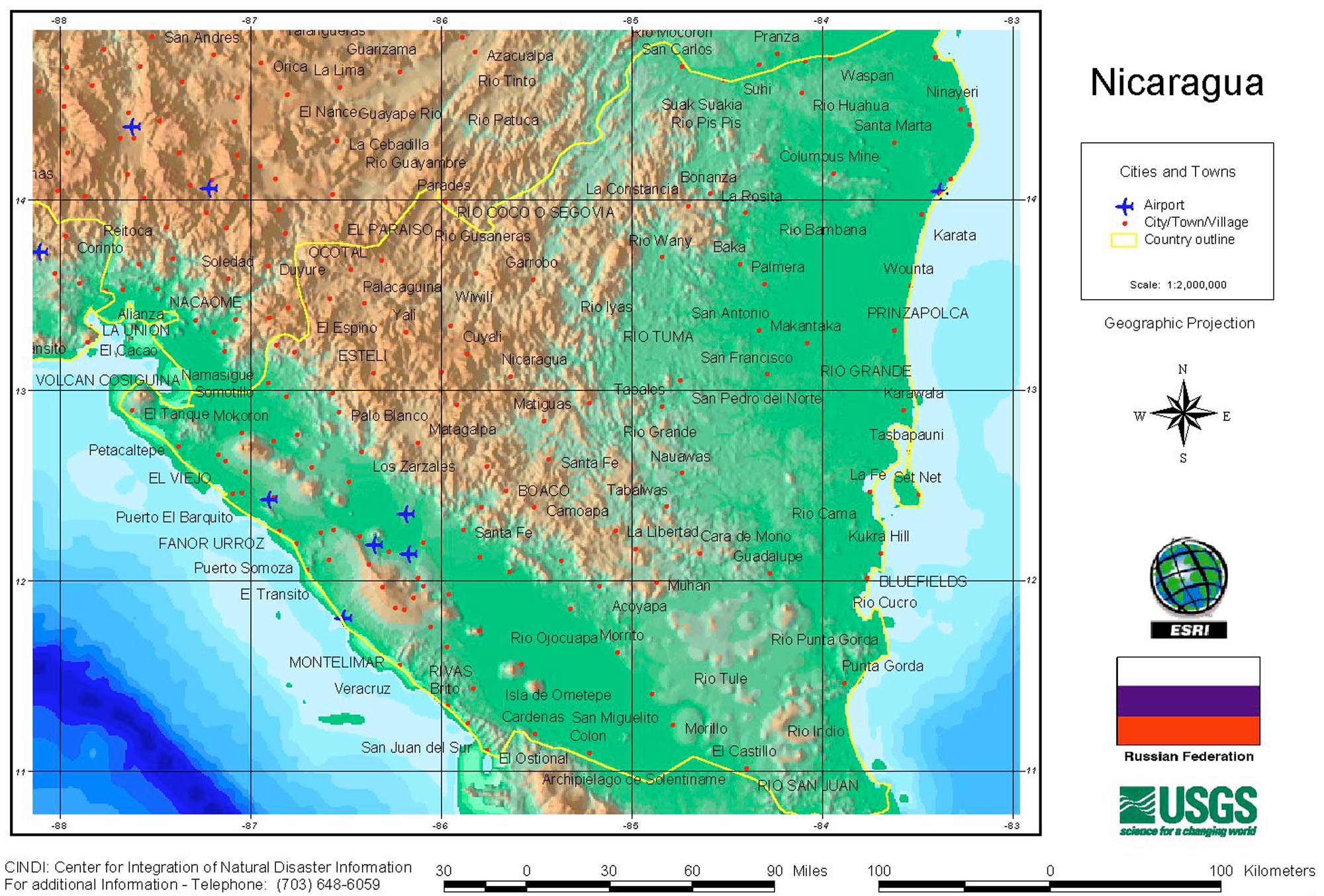
Nicaragua has very varied reliefs we can differentiate three units of relief: the volcanic sector of the Pacific, the central platform and the plains of the Caribbean.
The volcanic cord is located parallel to the coast from the Cosigüina peninsula, to the northwest, to the interior of Lake Nicaragua, on the island of Ometepe (Maribios chain). They are a series of 25 active and inactive volcanoes.
The central platform or of Segovia, is the mountainous zone of the country. It extends from northwest to southeast from Honduras to Costa Rica. The highest altitudes are the northwest, and descends progressively to the border with Costa Rica. In this unit is the hill Mogotón of 2,107 meters of altitude. The structure also descends as it approaches the Caribbean. The most important sierras are: Massif de Peñas Blancas, Isabelina, Dariense, Huapí and Yolaina.
The plains of the Caribbean extend from the foot of the central platform to the coast. It is a wide region of very recent fluvial deposits and with a strong marshy character. The structure also extends through Honduras, beyond Cape Gracias a Dios, and by Costa Rica. This is the traditional area where the Misquitos live, whose corruption of the word gives way to the coast of the Mosquitoes, with which the coastal zone is known.