Panama Economic Activity
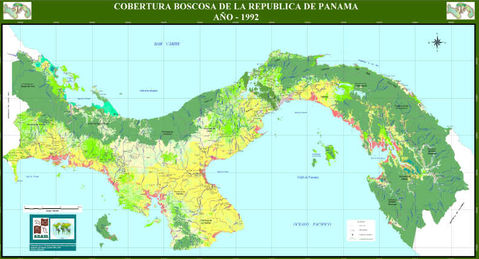
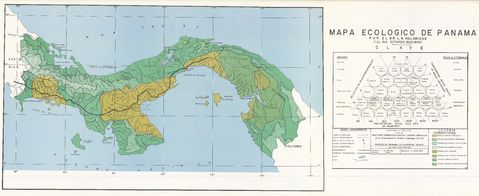
Panama Economic Activity Map 1981.
Panama's economy, due to its geographical position, is largely oriented towards services, banking, tourism and commerce. The service sector, including the Panama Canal, contributes 80% of its gross domestic product.
Panama is the tenth most unequal country in the world in 2016. The country is also a major tax haven that refuses to lift its banking secrecy. Panama is a member of the Inter-American Development Bank and its main trading partners are the United States, Canada, Venezuela, Colombia, Mexico, the Netherlands, Japan, Spain, Costa Rica and Germany.
In 2018, Panama produced 2.9 million tonnes of sugar cane, 400,000 tonnes of bananas, 314,000 tonnes of rice, 112,000 tonnes of corn, 109,000 tonnes of pineapple, 46,000 tonnes of palm oil, 40,000 tons of orange, in addition to small productions of other agricultural products such as watermelon, cassava, coconut, onion, potato, tomato, yam etc.
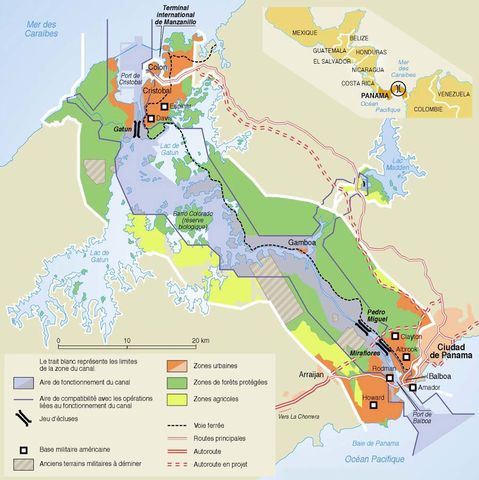
Cattle farming is developing rapidly. The fishing reserves (mainly shrimp) are important. Panama has large reserves of mahogany. The main industries are food processing, clothing manufacturing, paper and building materials. Panama also exports refined petroleum. The area around the canal is Panama's main economic zone. The canal generates revenue through transit taxes. Tourism completes the country's economic panorama. In the early 1990s, the government began a process of privatizing companies with the aim of reducing public spending.
Panama's economy, due to its geographical position, is largely oriented towards services, banking, tourism and commerce. The service sector, including the Panama Canal, contributes 80% of its gross domestic product.
Panama is the tenth most unequal country in the world in 2016. The country is also a major tax haven that refuses to lift its banking secrecy. Panama is a member of the Inter-American Development Bank and its main trading partners are the United States, Canada, Venezuela, Colombia, Mexico, the Netherlands, Japan, Spain, Costa Rica and Germany.
In 2018, Panama produced 2.9 million tonnes of sugar cane, 400,000 tonnes of bananas, 314,000 tonnes of rice, 112,000 tonnes of corn, 109,000 tonnes of pineapple, 46,000 tonnes of palm oil, 40,000 tons of orange, in addition to small productions of other agricultural products such as watermelon, cassava, coconut, onion, potato, tomato, yam etc.
Cattle farming is developing rapidly. The fishing reserves (mainly shrimp) are important. Panama has large reserves of mahogany. The main industries are food processing, clothing manufacturing, paper and building materials. Panama also exports refined petroleum. The area around the canal is Panama's main economic zone. The canal generates revenue through transit taxes. Tourism completes the country's economic panorama. In the early 1990s, the government began a process of privatizing companies with the aim of reducing public spending.